Stem Cell Therapy for Peripheral Neuropathy Latest Potential Safe & Long-Term Effective Treatment for Peripheral Neuropathy
What Is Peripheral Neuropathy and What Causes It?
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) is an umbrella term that refers to conditions of neuropathic pain experienced in part of the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system includes all of the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord, which are considered to be part of the central nervous system. PN may be caused by:
- Diabetes complications (diabetic neuropathy)
- Chemotherapy or drug side effects
- Trauma to a nerve
- Nerve compression, such as carpal tunnel syndrome
- Autoimmune attack of a nerve, such as Guillain-Barre syndrome
- HIV complications
- Vitamin deficiencies affecting nerves, such as a vitamin B12 deficiency
- Dental surgery
- Exposure to certain toxins, poisons, or chemicals
- Disorders or damages of the mitochondria, part of the cell that produces energy.
PN is most common in patients over 50, but it can occur to anyone at any time depending on the cause. Some causes of PN are temporary or can be reversed, while others, namely physical trauma, can be more difficult to treat.
Types of Peripheral Neuropathy
There are over 100 types of peripheral neuropathy. However, they can be broadly categorized into four groups, including motor, sensory, autonomic, and combination neuropathies, depending on the types of nerves affected. The type of nerves that are impaired will determine the symptoms. It is possible to experience symptoms from two or all three nerve categories depending on the cause of the PN.
Motor neuropathy
Motor neurons control movements like walking and lifting items. Therefore, symptoms of motor PN can include:
- Involuntary muscle twitches
- Muscle cramps
- Muscle shrinking
- Muscle weakness
Sensory neuropathy
Sensory nerves allow us to feel touch, temperature, and vibrations. Therefore, symptoms of sensory PN involve sensations from nerve damage that doesn’t have an ongoing cause, such as:
- Pain (without ongoing harm being inflicted), such as phantom limb pain
- Increased pain sensitivity
- Burning sensation
- Increased or decreased reaction to touch
- Numbness or lack of sensation
Autonomic nerve neuropathy
The autonomic nerves carry signals for processes in our bodies that we do not consciously think about, like sweating, breathing, and gut functions. Autonomic nerve neuropathy can be life-threatening.
Symptoms of autonomic PN can include:
- Increased sweating
- Increased or decreased intestinal function
- Difficulty regulating blood pressure
- Abnormal gut movement, including some types of irritable bowel syndrome, difficulty swallowing, and gastroparesis (slow stomach emptying)
Combination neuropathy
Combination neuropathy refers to the combination of two to three types of the above.
The Scientific Rationale Behind Stem Cell Therapy for Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) can make daily life difficult. Current treatment options may include pain medications with the risk of addiction or other side effects. Other options may also require a frequent return to office appointments for maintenance.
Stem cell therapy is a novel and effective treatment option for PN. It may require fewer visits and provide a longer duration of relief than conventional treatments for neuropathic pain.
Stem cells are immature (also called “undifferentiated) cells that can turn into several other cell types. They can also expand in numbers into more of the same stem cells.
For example, an adult stem cell that can become various tissue types can develop into a fat cell, neuron, cartilage, and many others. In stem cell therapy, these stem cells are placed in the area of need, where they can then replace degenerated tissues. The stem cells also go near areas of inflammation and damage to help promote repair and balance.
Stem cell therapy utilizes stem cells to help treat various neurological and non-neurological conditions. By injecting stem cells into the areas of concern, it can help repair tissue and benefit degenerative conditions like peripheral neuropathy.
Aside from repairing and replacing damaged tissues, these adult stem cells also help with:
- Reducing excess inflammation and overactive glial cell activity. Glial cells are immune cells in the nervous system that help clean up waste. Overactive glial cells can cause more damage and symptoms.
- Donating mitochondria to cells with damaged mitochondria. Most neurologic conditions, including peripheral neuropathy, involve damaged mitochondria in neurons. Also, treatments that improve mitochondrial health tend to help with these conditions.
Producing and releasing proteins that protect neurons and stimulate neuronal growth and repair
There are two types of stem cells: embryonic and adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells come from embryos, whereas adult stem cells come from adult tissues, including the umbilical cord.
At Nashville Regenerative, we use only adult stem cells harvested from the patient’s own body to treat the patient. This minimizes the risk of tissue rejection and eliminates any need for immunosuppressive drugs, unlike in other types of transplants.
Adult stem cells exist throughout your body. However, different kinds of stem cells exist in different places. Neural stem cells are not commonly used as they are deep in the brain and therefore too risky to retrieve. Adult stem cells that can become various tissue types are commonly used in stem cell therapy because they are easy to harvest and can develop into many important cell types.
These adult stem cells have been isolated from the following locations in the human body:
- Bone marrow
- Adipose (fat) tissue
- Periosteum (outside layer of bone)
- Tendon
- Lung
- Umbilical cord
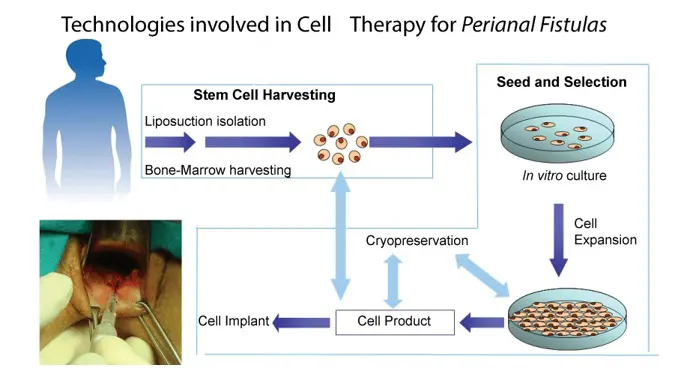
Bone marrow and fat tissues are common sites for stem cell harvesting. After harvesting, the stem cells can be isolated from your other tissues and used immediately, or they can be cultured in 6 - 8 weeks. When stem cells are cultured, they are grown in a nutrient medium, where they increase in numbers. This increased stem cell dose can then be injected, increasing the likelihood of beneficial results.
Currently, there is no cure for peripheral neuropathy (PN). Stem cell therapy for PN aims to repair the damage or dysfunction of impacted nerves using adult stem cells from the patient’s body. Stem cell therapy may also improve other disease processes, such as chronic inflammation and damaged mitochondria.
Stem cell therapy for peripheral neuropathy may help with:
- Improving movement (motor function)
- Reducing pain
- Improving daily function
- Other symptoms that reduce well-being in peripheral neuropathy, such as fatigue and mood issues.
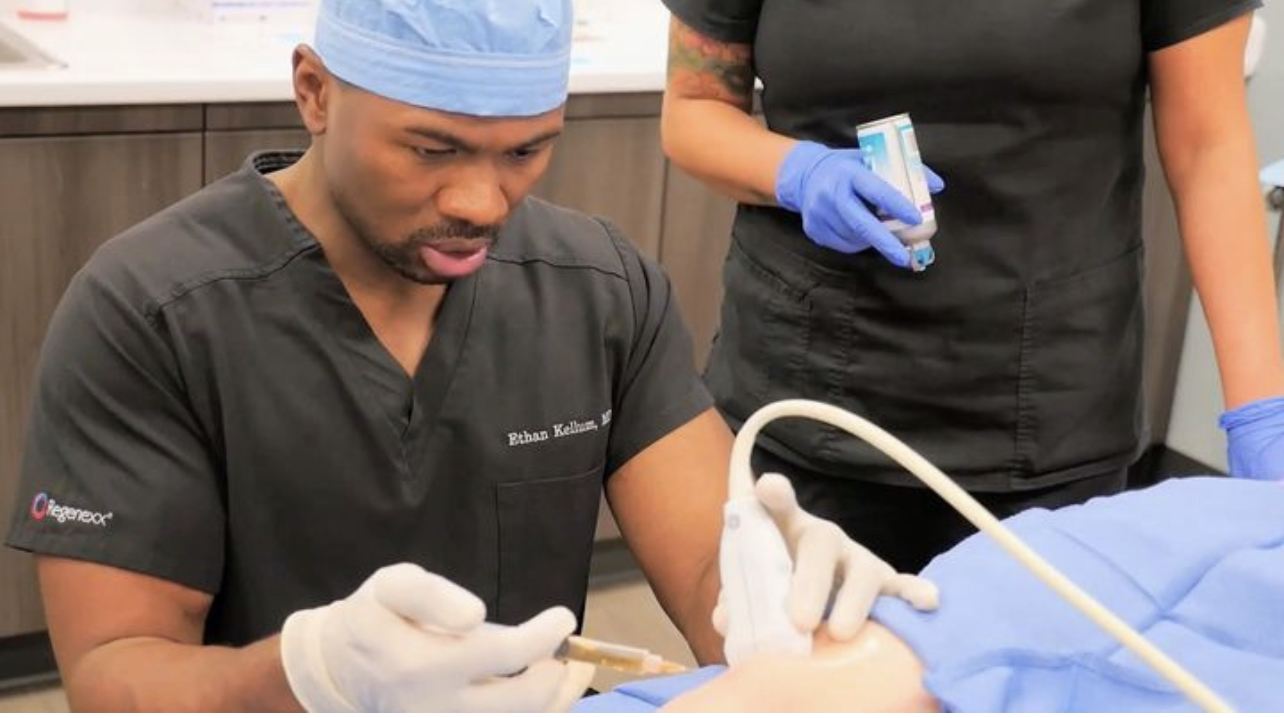
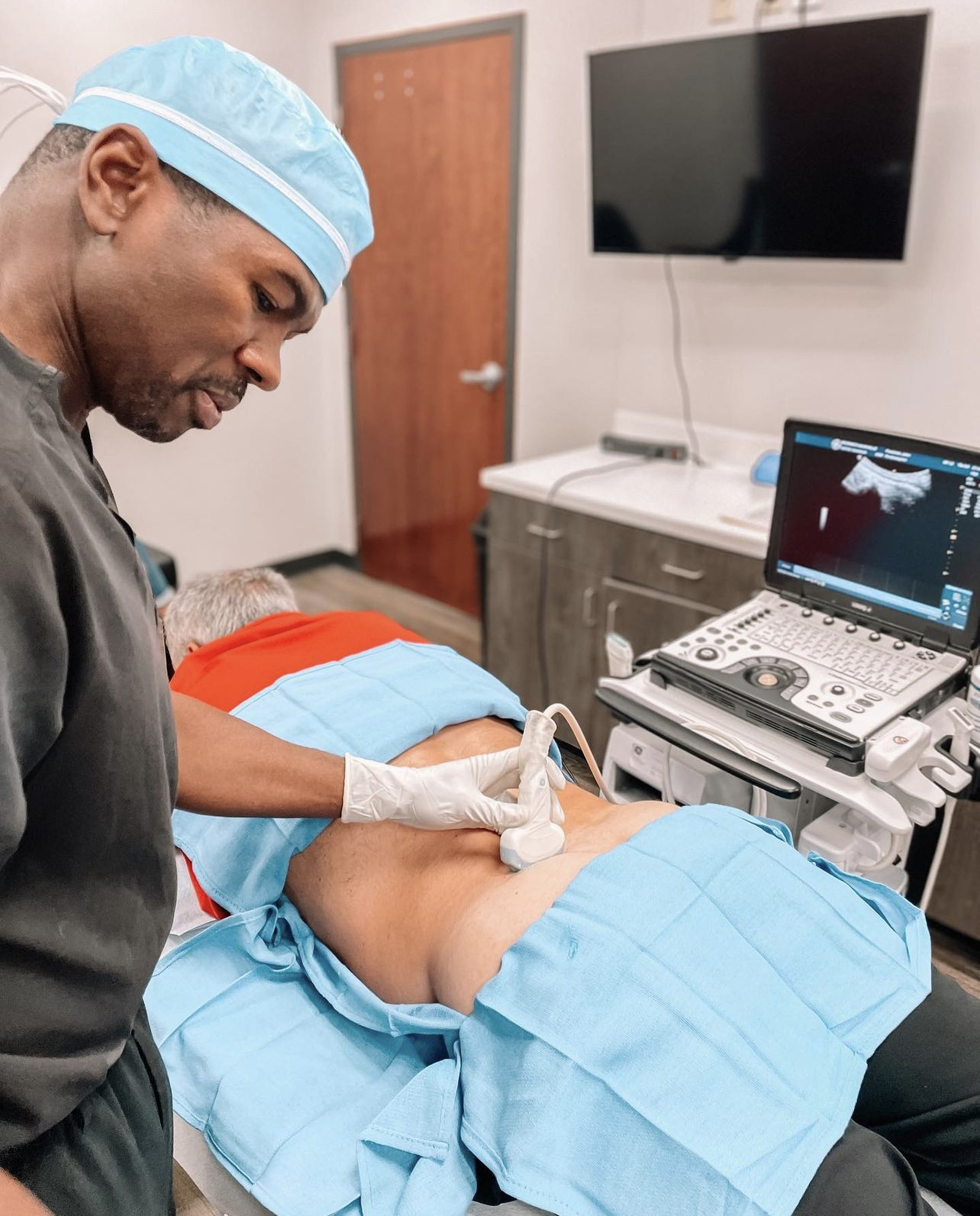
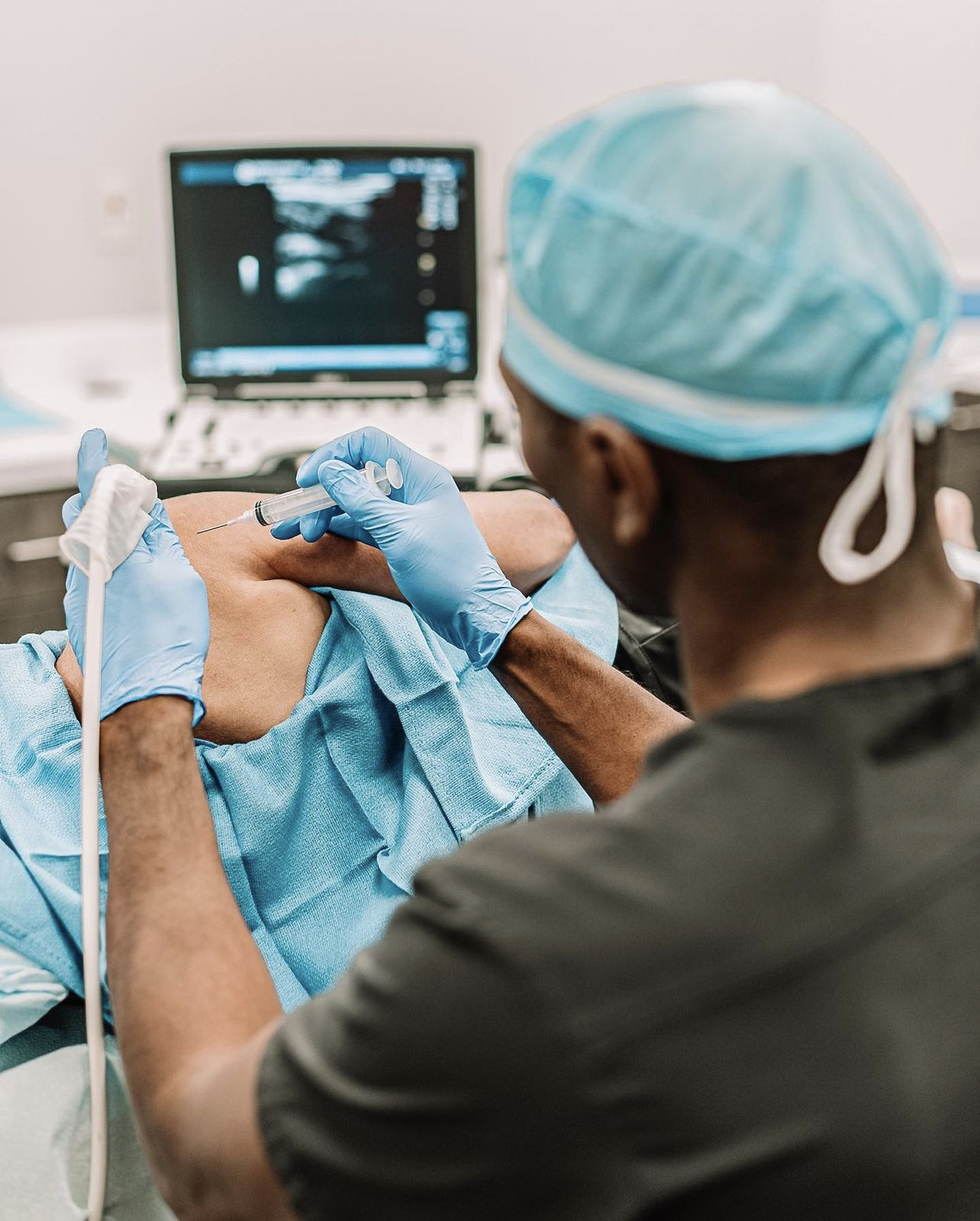
We harvest a mix of cells from fat tissues and bone marrow, and then separate the stem cells in the clinic. The stem cell suspension is then injected into the bloodstream and into the nervous system through the spine. Here, the stem cells can travel to the area of concern and begin their work. The stem cells may also be injected locally at the site of nerve injury.
For patients who need higher doses of stem cells, we culture their stem cells in the lab to increase the number of these stem cells. Our US-based stem cell lab facility is FDA-registered, ISO-7 certified and certified in Good Manufacturing Practices. We will then schedule a procedure to receive the stem cell treatment once the cultures are ready.
At Nashville Regenerative, stem cell therapy is accompanied by physical therapy to improve recovery. Stem cell therapy can be included as part of your holistic treatment plan .
Steps in Stem Cell Therapy for Peripheral Neuropathy
- Harvest stem cells from your bone and/or fat
- Inject some stem cells right away
- Culture some stem cells in our lab to increase cell numbers
- Get the stem cells back and inject the concentrated suspension (~6 - 8 weeks later)
-
Researchers have been exploring stem cell therapy for well over a decade. They’re also seeking to improve the efficacy of harvesting, delivering, and treating using stem cells.
Inflammation partly contributes to the pain in peripheral neuropathy. Glial cells are housekeepers that typically help clear away debris in the nervous system. However, when there is nerve injury, the glial cells can become hyperactive and release too many inflammatory molecules.
The FDA approved a research trial to use stem cells in two adults with sciatic nerve damage. The treatment involved using stem cells as part of a nerve graft. After treatment, the two adults had improved movement and sensation in the impacted areas.
Research has demonstrated that stem cell therapy can help reduce inflammation by migrating to the site of injury and decreasing glial cell activity at the site. In clinical trials, adult stem cell therapy reduced pain, unpleasant sensation reactions to benign touch, and discomfort with different temperatures.
One trial could reduce the pain medication needed in patients with trigeminal pain. All ten patients had chronic pain and were using prescription painkillers for their neuropathic pain. Researchers harvested stem cells from the patient's own fat after liposuction and injected the stem cells near the site of pain. After six months, the majority of patients had less pain and could reduce the dosage of their pain medication under medical guidance.
In clinical trials, researchers observed that stem cells help regenerate nerves when they have been crushed, damaged, and partially or fully severed. In 2019, the Japanese government approved stem cell therapy to treat spinal cord injury.
The longevity of relief is also important. Stem cell therapy relieved symptoms for longer than other treatments, without the same side effects. Some research suggests that adult stem cell treatments for spinal cord injury may deliver benefits for over two months.
While we need more trials in humans, animal studies and many small clinical trials have demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of stem cell therapy for peripheral neuropathy.
At Nashville Regenerative, we use evidence-based techniques based on clinical research and experience. Our non-surgical approach reduces recovery time. while the combination of stem cell therapy with physical therapy increases the holistic nature of patient treatment.
Safety is paramount at Nashville Regenerative. Our use of stem cells that come from your own body helps to minimize rejection and reduce the need for immunosuppression prior to treatment. Our inclusive approach helps to treat peripheral neuropathy in the least invasive manner possible.
Stem cell therapy may help at most stages and types of peripheral neuropathy. Whether it's a new injury or diagnosis, or this is a chronic presentation, you can consider including stem cell therapy as an option in your treatment plan.
One of stem cell therapy’s goals is to help potentially regenerate nerve tissue. While this goal is best achieved early on, stem cell therapy can still positively benefit long-term presentations.
Inflammation is not just present at the onset of symptoms. Inflammation and overactive glial cells can persist for years and may still benefit from stem cell therapy’s ability to reduce inflammation at the site of injury.
The cost depends on the specific treatment you will be undergoing and how many treatment sessions you need. Book a consultation with us today to get your personalized stem cell therapy treatment plan.
Typically, you will need one to two treatments, depending on the plan of care established between you and your doctor. All treatment appointments are in person, but the initial consultation and follow-up can be done by phone.
Some people come back for additional treatments over the course of months or years. This largely depends on the stage of your disease, how well you respond to the treatment, and what your treatment goals are.
Typically, you will need 1 - 2 treatments, depending on the plan of care established between you and your doctor. All treatment appointments are in person, but the initial consultation and follow-up can be done by phone.
Some people do come back for additional treatments over the course of months or years. This largely depends on the stage of your disease, how well you respond to the treatment, and what your treatment goals are.
Your Patient Journey with Stem Cell Therapy for Peripheral Neuropathy
Step 1: Application and initial consultation
Our questionnaire and initial consultation help us determine whether you’re a good candidate for stem cell therapy, along with the best treatment plans for you. Our patient advocate will walk you through the process, pricing, and payment plans.
Step 2: Physical exam
You’ll come in for a physical exam in preparation for the treatment and also to assess your current symptoms and health status.
Step 3: Stem cell collection
Your procedure will begin where we harvest cells from your bone marrow or fat tissues. We will then isolate the stem cells from these tissues in the clinic before administering your first treatment.
Step 4: Stem cell culture
If applicable, we will send your stem cells to the lab to expand them in numbers.
Step 5: Future treatments
Your future stem cell treatments will be done using your cultured stem cells.
Step 6: Follow-up appointments
Our team will keep in contact with you to monitor your treatment progress and support you through your recovery.
Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy vs Standard Treatments and Other Alternative Treatments for Peripheral Neuropathy
Current Standard-of-Care Treatments for Peripheral Neuropathy and Their Shortfalls
Treatments for peripheral neuropathy are typically classified under the treatment for neuropathic pain. Neuropathic pain includes the pain caused by nerves and can include both the peripheral and central nervous systems. While some treatment options are specific to the cause of peripheral neuropathy, many overlapping options exist for general peripheral neuropathy.
Chronic pain and nerve pain often result partly from the brain perceiving the pain sensations. Antidepressants are often the first-line pharmaceutical therapy for peripheral neuropathy. They are used for their ability to regulate the brain, which may impact how pain is perceived.
Side effects from antidepressant medications can include:
- Nausea
- Drowsiness
- Insomnia
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Sedation
- Increased blood pressure
- Anxiety
- Anorexia
- Weight gain
- Increased heart rate
- Blurry vision
Tricyclic antidepressants may regulate pain at doses 20-30% lower than those used for depression. This indicates that the use of antidepressants is for pain relief and not exclusively for their antidepressant properties. The drawback is that they can have an impact on mood and weight as a side effect.
Aside from helping to keep you looking younger, botox is also used for pain. Botox injections contain concentrated botulinum, a bacterial toxin, that causes paralysis in the area injected. The paralysis helps reduce pain signaling in the nerve and reduce pain sensation.
The major drawback of botox injections is that the benefit only lasts weeks to months. So, you will need regular injections to keep the pain at bay. Frequent botox injections can also destroy nearby tissue over time
Gabapentinoids like gabapentin and pregabalin are often prescribed for peripheral neuropathic pain. These medications work by reducing nerve signals. If there are fewer signals to the brain, then there is a reduced sensation of pain overall.
Side effects from gabapentinoids can include:
- Tremors
- Stomach upset
- Vision changes
- Weight gain
- Edema or swelling of the limbs
- Sedation
- Dry mouth
Opioids have been used for centuries for pain relief. Opioids like morphine and fentanyl can make excruciating pain bearable.
They are currently not considered first-line by most prescribing physicians due to their strongly addictive nature. The increasing opioid crisis is also raising alarm bells over their use as a prescription medication without adequate screening and follow-up.
Unpleasant side effects of opioids include:
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Drowsiness
- Allergic reactions
- Addiction
- Sedation
Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen and acetaminophen are readily available and often abused. The pain experienced with peripheral neuropathy can be excruciating. It is easy to reach for the bottle of painkillers found in most household medicine cabinets.
While painkillers are helpful for minor injuries, they may not be enough to ease the pain of peripheral neuropathy. This leads to an increased dose in an attempt to find relief.
Acetaminophen can damage the liver, especially with chronic use or over four grams (4000 milligrams) per day. Most tablets range between 325-600 mg.
Physical therapy aims to improve peripheral neuropathy by using exercise and manual work on the muscles, joints, and nerves. This type of therapy often requires regular clinic visits. While physical therapy may improve pain and overall well-being, it doesn’t directly repair the damaged nerves.
Physical therapists may use the following techniques:
- Acupuncture
- Exercise
- Massage
- Osteopathy
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
- Yoga
Physical therapy may be even more helpful when combined with stem cell therapy.
Currently, there is no objective test or measurement for pain beyond the patient’s self-reported. Therefore, the medical industry has often considered it a psychiatric condition.
Often, chronic pain happens due to the brain rewiring to become more sensitive to pain (central sensitization). So, the pain may not correspond to the physical damage. This type of brain rewiring is worse with more severe stress. Peripheral neuropathy can cause stress that makes the brain more likely to rewire for more pain sensations. Thinking negatively about the pain can also make it worse.
Psychotherapy helps patients understand and cope with their pain. Psychotherapy can also reduce the central sensitization and change patients’ mindsets toward overcoming their pain limits.
Psychotherapy generally includes one or more of the following therapy types:
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
- Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)
- Mindfulness-Based Therapy
- Operant Behavioural Therapy
Patients experiencing chronic peripheral neuropathy may also experience anxiety, depression or PTSD as a result of their lived experience with pain. Psychotherapy is useful in addressing these comorbid mental health concerns
Spinal cord stimulation involves the implantation of an electrical device along the spinal cord. The device then emits low-level electrical currents to help mitigate the pain nerve signals that the damaged nerve sends to the brain.
This relatively new therapy can come with the following complications:
- Infection at the site of implantation
- Device breakage from a fall or intense physical activity
- Device migration away from the site of implantation, requiring follow-up surgery
- Further injury to the spinal cord
There are several different options for topical treatment, including topical lidocaine, which numbs the area. While these treatments generally carry only minor full-body side effects, they can still cause topical reactions like rashes. The problem with these treatments is that they generally do not last very long and therefore require frequent application.
Why Nashville Integrative Therapy?
We are passionate about delivering safe and effective treatments to our patients, especially when standard-of-care treatments fall short. Over the years, we’ve seen the immense life-changing benefits of stem cell therapy first-hand and we’re passionate about making it available to you.

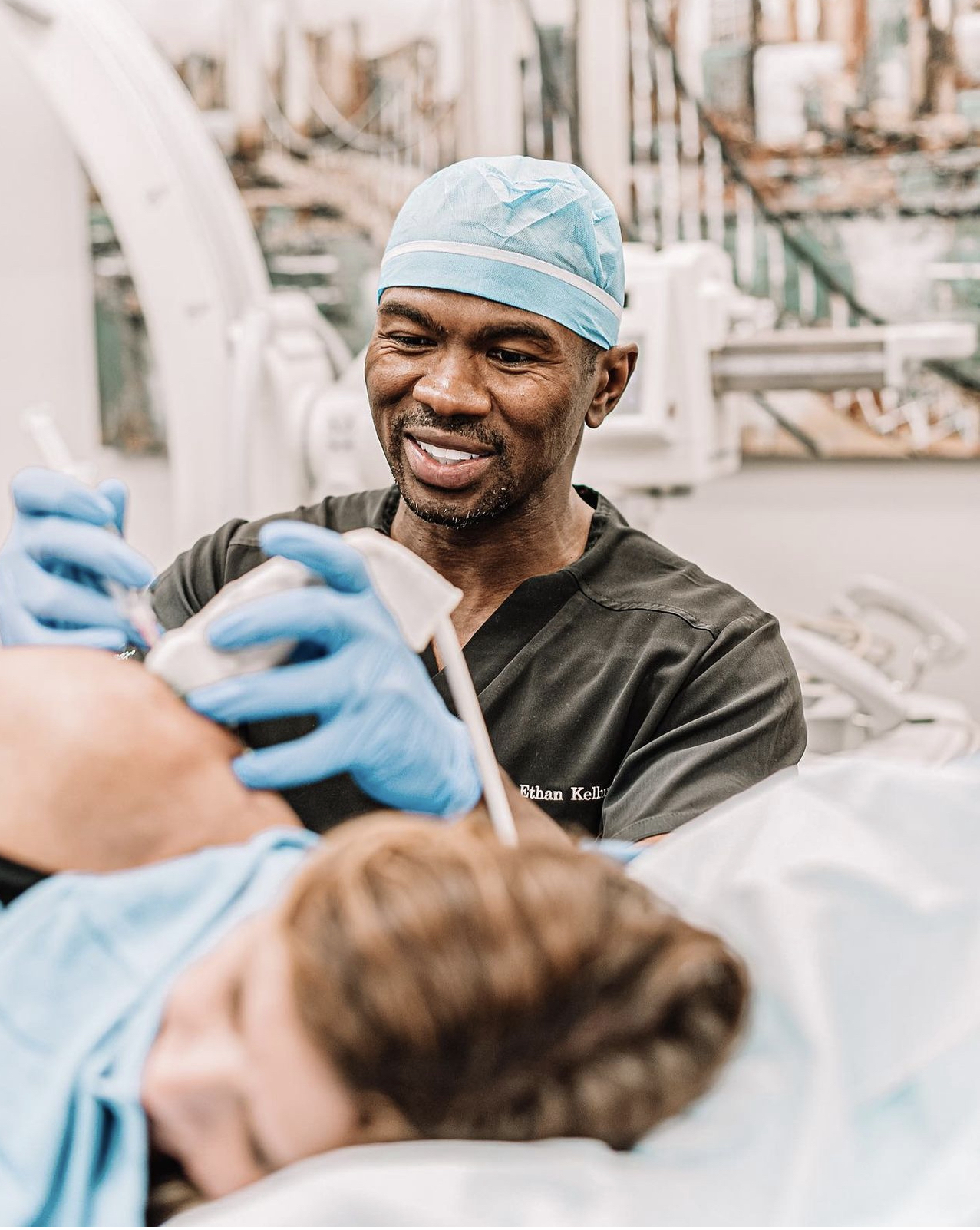
About Dr. Ethan Kellum, MD
Dr. Ethan Kellum is a pioneer in interventional and regenerative orthopedics. As a sports medicine specialist who is fellowship-trained in orthopedic surgery, Dr. Kellum is an expert in musculoskeletal injuries and joint conditions. Although he still performs shoulder and knee surgeries, his main focus has become regenerative medicine, especially stem cell therapy, to keep patients out of the operating room.
Dr. Kellum is a native of Henderson, Tennessee and attended Jackson Christian School and Freed-Hardeman University. He earned a medical degree from the University of Tennessee Health Science Center College of Medicine in Memphis. After a residency in orthopedic surgery at the Medical College of Georgia, he then completed a surgical fellowship in sports medicine, shoulder, and advanced arthroscopy at the renowned New England Baptist Hospital and Boston Children’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. During his fellowship, he served as assistant team physician for the NBA’s Boston Celtics, and for both Harvard and Tufts University athletics. Dr. Kellum is a member of the prestigious Alpha Omega Alpha Medical Honor Society. Dr. Kellum has been actively involved in orthopedic surgery research throughout his medical career. He also has authored and co-authored several peer-reviewed orthopedic surgery articles and book chapters.
Beyond his credentials, Dr. Kellum is a compassionate, committed surgeon who has care and love for each and every patient he sees. It is Dr. Kellum’s passion to create an environment that treats and cares for the whole patient- mind, body and soul holistically. He aspires to build the full-body health and longevity of each of his patients through regenerative orthopedics, nutrition, exercise and complementary medicine. Dr. Kellum works to create an innovative and patient-centered atmosphere that feels like home.
What our patients are saying about our stem cell therapy
Got questions?
Speak to our patient advocate
Frequently Asked Questions
The FDA has not currently approved the majority of stem cell therapies in the U.S., despite demonstrated research of safety and efficacy. “Currently, the only stem cell treatments approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are products that treat certain cancers, and disorders of the blood and immune system.”
Stem cell therapy is currently not covered by insurance. As more research is done and the efficacy becomes clearer and it is FDA approved, this should change.
We offer payment plans for those in need. Book a consultation to see how we can serve you.
Stem cell therapies that use your own cells (autologous) to stimulate new cell and tissue growth are completely ethical. They also have a lower risk of immune system rejection.
The use of mesenchymal stem cells does not involve embryos or fetuses. These stem cells are harvested and cultured from your own tissue.
This varies by person. Benefits may be seen in a matter of a few months and may continue to stay improved for many years.
The most common side effect is an injection site reaction. There is the possibility, even with your own cells, that there can be immune system reactions to the injected solution.
Most potential serious side effects of stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease are theoretical. The concerns raised but which have never actually occurred include a potential risk of tumor formation from stem cells that begin to grow out of control.
It’s possible that your medication needs will change after receiving stem cell treatments, but the effect will be highly individual. We always recommend that our patients work with their doctors to monitor their symptoms and possibly adjust their medications. Please do not change or come off your medications without speaking to your prescribing physician.
In the clinical literature, some Parkinson’s patients have been able to taper off their medications after receiving sufficient stem cell therapy. In a case study, a Parkinson’s patient was able to wean off their medication after 6 months of stem cell therapy treatment. The researchers detected dopamine production from transplanted stem cells as long as 10 years after the treatment.
The only way to know for sure if you are a good candidate is to schedule a consultation and have the doctor assess your health and symptoms. After this, you will be given the options that are best for your individual scenario.
1. Castelli, G., Desai, K. M. & Cantone, R. E. Peripheral Neuropathy: Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis. Am. Fam. Physician 102, 732–739 (2020).
2. Pareyson, D., Piscosquito, G., Moroni, I., Salsano, E. & Zeviani, M. Peripheral neuropathy in mitochondrial disorders. Lancet Neurol. 12, 1011–1024 (2013).
3. Sommer, C. et al. Polyneuropathies. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 115, 83–90 (2018).
4. The Royal Australian College of general Practitioners. Paraesthesia and peripheral neuropathy. Australian Family Physician https://www.racgp.org.au/afp/2015/march/paraesthesia-and-peripheral-neuropathy/.
5. Joshi, H. P. et al. Stem Cell Therapy for Modulating Neuroinflammation in Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, (2021).
6. English, K. & Barton, M. C. HDAC6: A Key Link Between Mitochondria and Development of Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 14, 684714 (2021).
7. Paradisi, M. et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells produce bioactive neurotrophic factors: source, individual variability and differentiation issues. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 27, 391–402 (2014).
8. Alessandrini, M., Preynat-Seauve, O., De Bruin, K. & Pepper, M. S. Stem cell therapy for neurological disorders. S. Afr. Med. J. 109, 70–77 (2019).
9. da Silva Meirelles, L., Caplan, A. I. & Nardi, N. B. In search of the in vivo identity of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 26, 2287–2299 (2008).
10. White, C. M., van Doorn, P. A., Garssen, M. P. J. & Stockley, R. C. Interventions for fatigue in peripheral neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. CD008146 (2014).
11. Kubiak, C. A. et al. Stem-cell-based therapies to enhance peripheral nerve regeneration. Muscle Nerve 61, 449–459 (2020).
12. Vickers, E. R., Karsten, E., Flood, J. & Lilischkis, R. A preliminary report on stem cell therapy for neuropathic pain in humans. J. Pain Res. 7, 255–263 (2014).
13. Ford, E. et al. Human Pluripotent Stem Cells-Based Therapies for Neurodegenerative Diseases: Current Status and Challenges. Cells 9, (2020).
14. Fortino, V. R., Pelaez, D. & Cheung, H. S. Concise review: stem cell therapies for neuropathic pain. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2, 394–399 (2013).
15. Bates, D. et al. A Comprehensive Algorithm for Management of Neuropathic Pain. Pain Med. 20, S2–S12 (2019).
16. Acetaminophen. (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2016).
17. Finnerup, N. B., Kuner, R. & Jensen, T. S. Neuropathic Pain: From Mechanisms to Treatment. Physiol. Rev. 101, 259–301 (2021).
18. Sturgeon, J. A. Psychological therapies for the management of chronic pain. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 7, 115–124 (2014).
19. Foley, H. E., Knight, J. C., Ploughman, M., Asghari, S. & Audas, R. Association of chronic pain with comorbidities and health care utilization: a retrospective cohort study using health administrative data. Pain 162, 2737–2749 (2021).
20. Complications of spinal cord stimulator implantation. The American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine (ASRA) https://www.asra.com/news-publications/asra-newsletter/newsletter-item/asra-news/2019/08/07/complications-of-spinal-cord-stimulator-implantation.
21. Stem cell and exosome products. https://www.cdc.gov/hai/outbreaks/stem-cell-products.html (2019).
Patients Worldwide have been treated at Nashville Regenerative Orthopedics
Are You a Candidate?
Our in-house science team has researched the many types of stem cells available today. Together with our clinical teams, we believe that using your own stem cells are the safest, most effective therapy choice for your body and your health.
Our research-based therapies use your own stem cells to accelerate your healing — without surgery.
Request an Introductory Patient Package
Receive an introductory patient package by email.